Projects Undergoing

🧑🏻💻 🟩🟩🟩🟩⬜️
Segmentation Only Uses Sparse Annotations: Unified Weakly and Semi-Supervised Segmentation in Medical Image
(A joint work with The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. The paper is submitted to Medical Image Analysis🤞.)
Abstract Since segmentation labeling is usually time-consuming and annotating medical images requires professional expertise. It is laborious to obtain a large-scale, high-quality annotated segmentation dataset of medical images. We propose a novel weakly- and semi-supervised framework named SOUSA, aiming at learning from a small set of sparse annotated data and a large amount of unlabeled data. The proposed framework contains the teacher model and student model. The student model is weakly supervised by scribbles and a Geodesic distance map derived from scribble and the input image. Meanwhile, a large amount of unlabeled data with different perturbations are fed to both student and teacher models, and the consistency of their output predictions is imposed by Mean Square Error (MSE) loss and a carefully designed Multi-angle Projection Reconstruction (MPR) loss. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the robustness and generalization ability of our proposed method. Results show that our method outperforms weakly- and semi-supervised SOTA methods on multiple datasets. Furthermore, our method achieves a competitive or higher performance than some fully supervised methods when the size of the dataset is limited.
🧑🏻💻 🟩🟩🟩⬜️⬜️
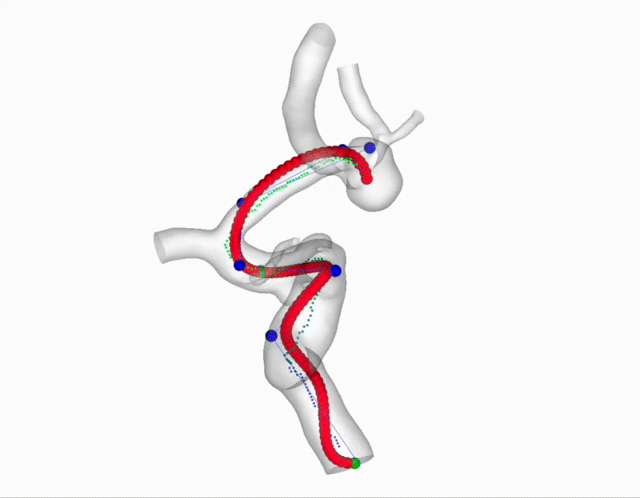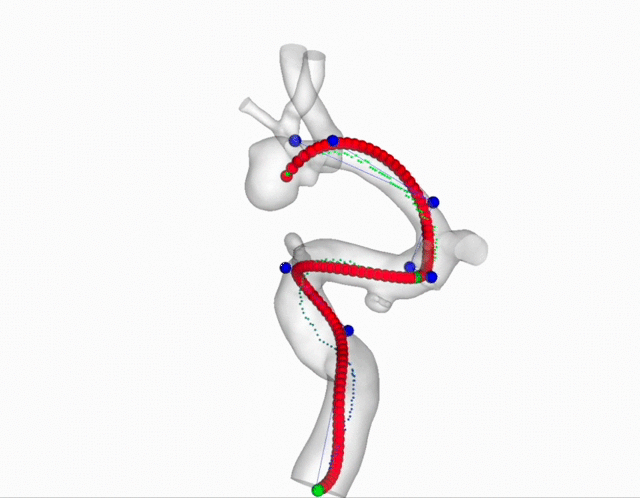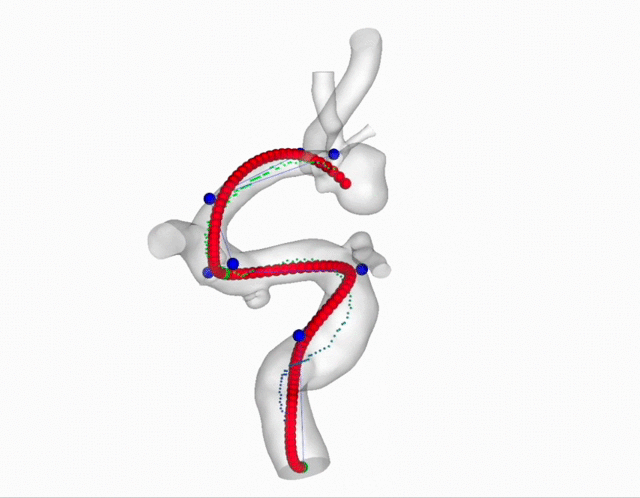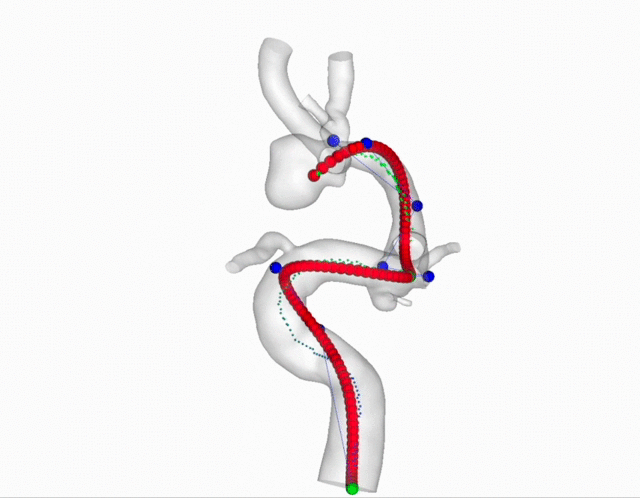
Carotid Plaques Segmentation and Stenosis Degree Classification
Internal Carotid Artery plaques is an significant public health problem which is highly related to ischemic stroke. In this project, we aim to segment the carotid plaques from CTA images. Then based on the segmentation results, we provide a new method to estimate the stenosis degree for each plaque area.
🧑🏻💻 🟩🟩⬜️⬜️⬜️
Micro Catheter Shaping
Publications

Fully Test-time Adaptation for Image Segmentation
M Hu , T Song, Y Gu, X Luo, J Chen, Y Chen, Y Zhang, S Zhang
International Conference on Medical Image Computing & Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2021)
Abstract When adopting a model from the source domain to the target domain, its performance usually degrades due to the domain shift problem. In clinical practice, the source data usually cannot be accessed during adaptation for privacy policy and the label for the target domain is in shortage because of the high cost of professional labeling. Therefore, it is worth considering how to efficiently adopt a pretrained model with only unlabeled data from the target domain. In this paper, we propose a novel fully test-time unsupervised adaptation method for image segmentation based on Regional Nuclear-norm (RN) and Contour Regularization (CR). The RN loss is specially designed for segmentation tasks to efficiently improve discriminability and diversity of prediction. The CR loss constrains the continuity and connectivity to enhance the relevance between pixels and their neighbors. Instead of retraining all pa- rameters, we modify only the parameters in batch normalization layers with only a few epochs. We demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method in the pancreas and liver segmentation dataset from the Medical Segmentation Decathlon and CHAOS challenge.

Knowledge Distillation from Multi-modal to Mono-modal Segmentation Networks
M Hu, M Maillard, Y Zhang, T Ciceri, G La Barbera, I Bloch, P Gori
International Conference on Medical Image Computing & Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2020)
Abstract The joint use of multiple imaging modalities for medical image segmentation has been widely studied in recent years. The fusion of information from different modalities has demonstrated to improve the segmentation accuracy, with respect to mono-modal segmentations, in several applications. However, acquiring multiple modalities is usually not possible in a clinical setting due to a limited number of physicians and scanners, and to limit costs and scan time. Most of the time, only one modality is acquired. In this paper, we propose KD-Net, a framework to transfer knowledge from a trained multi-modal network (teacher) to a mono-modal one (student). The proposed method is an adaptation of the generalized distillation framework where the student network is trained on a subset (1 modality) of the teacher’s inputs (n modalities). We illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework in brain tumor segmentation with the BraTS 2018 dataset. Using different architectures, we show that the student network effectively learns from the teacher and always outperforms the baseline mono-modal network in terms of segmentation accuracy.